Optimizing Aircraft MRO Operations: Strategies for Efficiency and Cost Savings

Global MRO Aircraft market insights
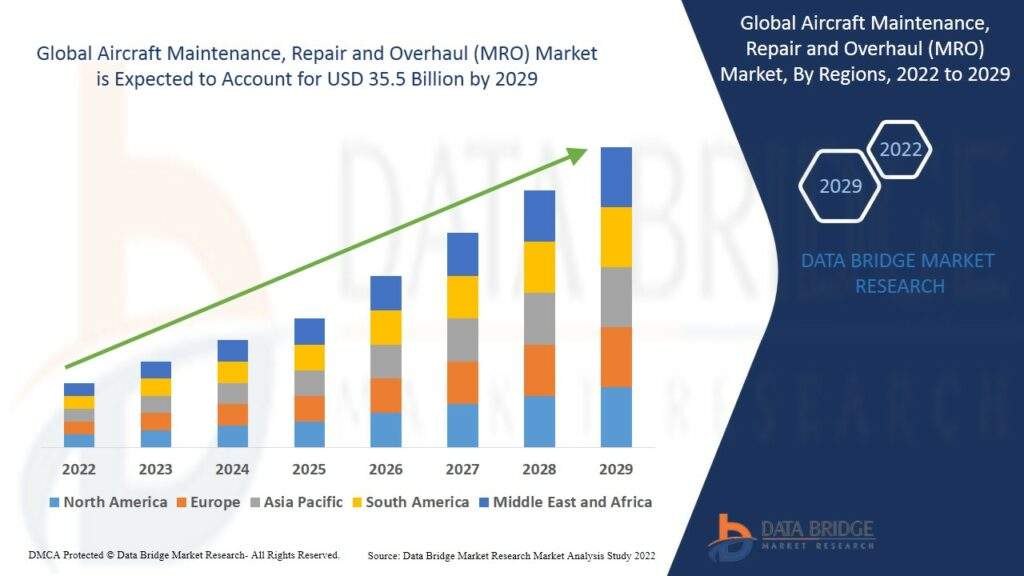
Data Bridge Market Research analyses that the aircraft MRO market(maintenance, repair, and overhaul) is expected to gain market growth in the forecast period of 2022 to 2029. It will reach an estimated value of USD 35.5 billion by 2029 and grow at a CAGR of 1.5% in the above-mentioned forecast period.
Introduction to Aircraft MRO
- Aircraft MRO (Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul) is a critical aspect of the aviation industry that involves the maintenance, repair, and overhaul of aircraft to ensure their safe and reliable operation. It encompasses a wide range of activities, from routine inspections and preventive maintenance to complex repairs and major overhauls of aircraft components and systems.
- Aircraft MRO is essential to ensure the safety and airworthiness of aircraft, as well as to maintain their performance and operational efficiency. It is regulated by national aviation authorities and international organizations, such as the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States, the European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) in Europe, and the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) globally, to ensure compliance with strict standards and regulations.
Types of Aircraft MRO
- Aircraft MRO can be categorized into various types, including line maintenance, base maintenance, and overhaul. Line maintenance involves routine inspections, repairs, and maintenance tasks performed on aircraft between flights or during layovers, while base maintenance encompasses more extensive maintenance and repairs carried out in a dedicated maintenance facility. Overhaul refers to the extensive disassembly, inspection, repair, and reassembly of major aircraft components, such as engines, landing gear, and avionics, to extend their service life.
- Aircraft MRO providers can be independent companies specializing in maintenance services, or they can be part of an airline’s in-house maintenance department. These providers employ highly skilled and certified technicians who use specialized tools, equipment, and procedures to inspect, repair, and overhaul aircraft components according to the manufacturers’ recommendations and regulatory requirements.
Operations of Aircraft MRO
Aircraft MRO operations involve a wide range of activities that are essential for the maintenance, repair, and overhaul of aircraft to ensure their continued airworthiness and safe operation. These operations are carried out by skilled technicians and engineers, using specialized tools, equipment, and procedures, and are typically regulated by aviation authorities and organizations to ensure compliance with strict standards.
Inspections
Regular inspections are performed to assess the condition of aircraft components and systems, identify any signs of wear, damage, or corrosion, and determine the need for maintenance or repair. Inspections can be visual, non-destructive testing (NDT), or using specialized equipment such as borescopes, ultrasonic testers, and X-ray machines.
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance involves scheduled maintenance tasks to prevent potential issues and ensure the reliability and longevity of aircraft components. This can include tasks such as lubrication, filter replacement, cleaning, calibration, and functional checks to ensure that components are operating within specified limits.
Repairs
Repairs are performed to fix identified issues during inspections or when defects are discovered during routine operations. Repairs can involve repairing or replacing damaged or worn-out components, fixing structural damage, repairing electrical or avionic systems, and addressing other issues that affect the airworthiness of the aircraft.
Overhauls
Overhauls involve extensive disassembly, inspection, repair, and reassembly of major aircraft components or systems to restore them to their original performance specifications. Overhauls are typically performed at predetermined intervals or when components have reached their service life limits, and can include tasks such as replacement of worn-out parts, refurbishment, and testing.
Modifications and Upgrades
Aircraft MRO operations can also include modifications and upgrades to aircraft components or systems to improve performance, comply with regulatory requirements, or enhance safety features. This can involve installing new equipment, upgrading avionics, modifying structural components, or integrating new technologies.
Documentation and Record-Keeping
Proper documentation and record-keeping are critical in aircraft MRO operations to maintain traceability, compliance, and accountability. This includes recording all maintenance tasks, inspections, repairs, modifications, and upgrades performed on the aircraft, as well as maintaining technical manuals, maintenance records, and other relevant documentation.
Logistics and Supply Chain Management
MRO operations also involve managing the logistics and supply chain for aircraft parts, tools, and equipment. This includes procurement, inventory management, warehousing, transportation, and coordination with suppliers and vendors to ensure timely availability of required parts and materials.
Quality Assurance and Compliance
Aircraft MRO operations are subject to strict quality assurance and compliance requirements, including adherence to regulatory standards, manufacturer specifications, and industry best practices. This involves implementing quality control measures, conducting audits, and maintaining certifications to ensure that the maintenance, repair, and overhaul activities are performed to the highest standards of safety and quality.
Testing and Certification
Before an aircraft can be returned to service after maintenance, repair, or overhaul, it must undergo thorough testing and certification to ensure that it meets all regulatory requirements and performance standards. This includes functional testing, performance testing, and verification of compliance with applicable regulations and manufacturer’s specifications.
Safety and Environmental Compliance
Safety and environmental compliance are integral to aircraft MRO operations. This involves following strict safety protocols, using appropriate protective equipment, and adhering to environmental regulations for handling hazardous materials, waste disposal, and emissions control.
Optimizing aircraft MRO (Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul) operations for efficiency and cost savings
Data-Driven Decision Making
Utilize data analytics and predictive maintenance techniques to make informed decisions about maintenance tasks. Collect and analyze data from aircraft sensors, maintenance records, and other sources to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies that can help optimize maintenance schedules, reduce unnecessary maintenance, and improve operational efficiency.
Lean and Six Sigma Principles
Implement Lean and Six Sigma principles to streamline MRO processes, eliminate waste, and reduce unnecessary costs. Identify and eliminate non-value-added activities, optimize workflows, and standardize processes to improve productivity, reduce cycle times, and minimize errors.
Integrated Supply Chain Management
Optimize the supply chain for aircraft parts and materials by leveraging technology, implementing efficient procurement practices, optimizing inventory levels, and collaborating closely with suppliers. This can help reduce lead times, minimize stockouts, and ensure the timely availability of required parts while managing costs.
Training and Development:
Invest in training and development programs for MRO technicians and engineers to enhance their skills and expertise. Well-trained and competent staff can perform maintenance tasks more efficiently, reduce errors, and minimize rework, leading to improved productivity and cost savings.
Asset Management
Implement effective asset management practices to optimize the lifecycle of aircraft components and systems. This includes proper maintenance planning, condition-based maintenance, and proactive replacement of components before they reach their end of life. Optimizing asset management can reduce unscheduled downtime, increase component reliability, and extend the service life of assets, resulting in cost savings.
Automation and Technology
Leverage automation and technology solutions to streamline MRO operations. This can include using computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS) for scheduling and tracking maintenance tasks, utilizing robotic process automation (RPA) for repetitive tasks, and employing advanced diagnostics and prognostics tools for predictive maintenance. Automation and technology can reduce human errors, improve efficiency, and optimize maintenance processes.
Collaborative Partnerships
Establish collaborative partnerships with original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), airlines, and other MRO providers to share knowledge, best practices, and resources. Collaborative partnerships can lead to cost savings through economies of scale, shared resources, and mutual support in terms of maintenance planning, component pooling, and technical expertise.
Continuous Improvement
Implement a culture of continuous improvement within the MRO organization to encourage feedback, identify areas for improvement, and implement changes iteratively. Regularly review and update processes, procedures, and practices to identify and address inefficiencies, reduce costs, and optimize operations.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure strict compliance with regulatory requirements and standards to avoid penalties, fines, and disruptions to operations. Stay updated with regulatory changes and proactively implement necessary measures to comply with regulations, certifications, and industry standards.
Environmental Sustainability
Implement environmentally sustainable practices in MRO operations, such as waste reduction, energy conservation, and emissions control. This can lead to cost savings through reduced waste disposal costs, energy-efficient processes, and compliance with environmental regulations.